交换两个数的值 元组解构 该方法也会创建一个临时变量(元组)
异或 a,b 不能是同一地址。由于异或的特性,如果两个是同一地址会导致输出为0
1 2 3 a = a ^ b; b = a ^ b; a = a ^ b;
拓展:异或
相同则为0,不同则为1,可以理解成“不进位的加法”
0 ^ N = N N ^ N = 0
满足交换律和结合律
加减 同样a,b不能是同一地址,不然在第二步的时候,自己减自己等于0
1 2 3 a = a + b; b = a - b; a = a - b;
时间复杂度 常数操作的次数
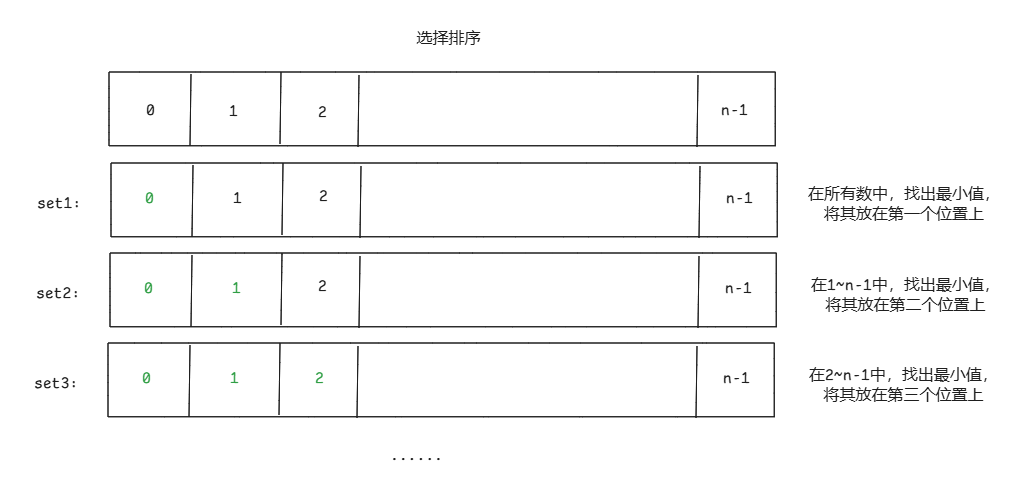
排序算法 选择排序 简单选出最小的数,将其放置在最前面
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 static void SelectionSort (int [] arr{ if (arr == null || arr.Length < 2 ) return ; for (int i = 0 ; i < arr.Length; i++) { int minIndex = i; for (int j = i + 1 ; j < arr.Length; j++) { if (arr[j] < arr[minIndex]) minIndex = j; } Swap(arr, i, minIndex); } } static void Swap (int [] arr, int a, int b{ int temp = arr[a]; arr[a] = arr[b]; arr[b] = temp; } int [] nums = new [] { 5 , 2 , 7 , 3 , 9 , 1 , 8 , 6 };nums = QuickSort(nums); Console.WriteLine(string .Join(", " , nums));
时间复杂度计算:
set1:
set2:
……
由等差数列公式可知:
获取数值共:n(n+1)/2次
比较共:n(n+1)/2次
交换共:n次
三者相加最大的阶乘为2,所以时间复杂度为O(n^2)
拓展:等差数列公式
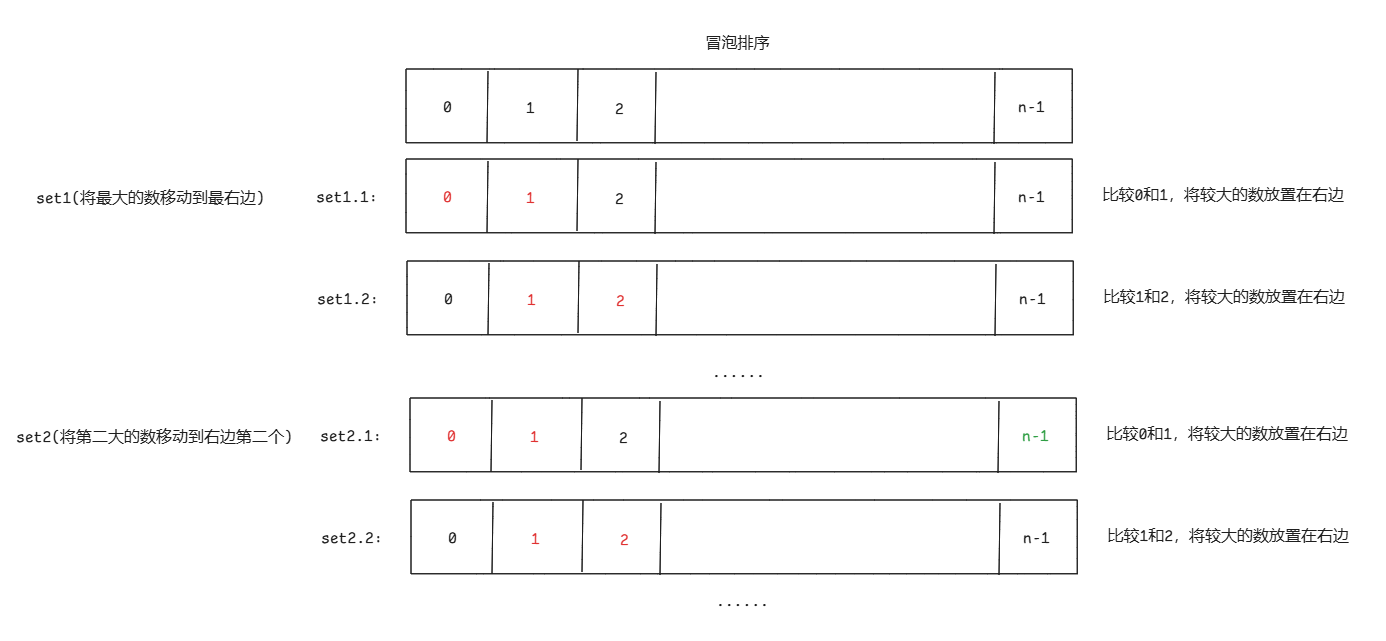
冒泡排序 相邻的两个数相比较,一步一步的将最大的数移动到最右边
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 static void BubbleSort (int [] arr{ if (arr == null || arr.Length < 2 ) return ; for (int k = 0 ; k < arr.Length; k++) { for (int i = 0 ; i < arr.Length - 1 ; i++) { if (arr[i] > arr[i + 1 ]) { Swap(arr, i, i + 1 ); } } } } static void Swap (int [] arr, int a, int b{ arr[a] = arr[a] ^ arr[b]; arr[b] = arr[a] ^ arr[b]; arr[a] = arr[a] ^ arr[b]; }
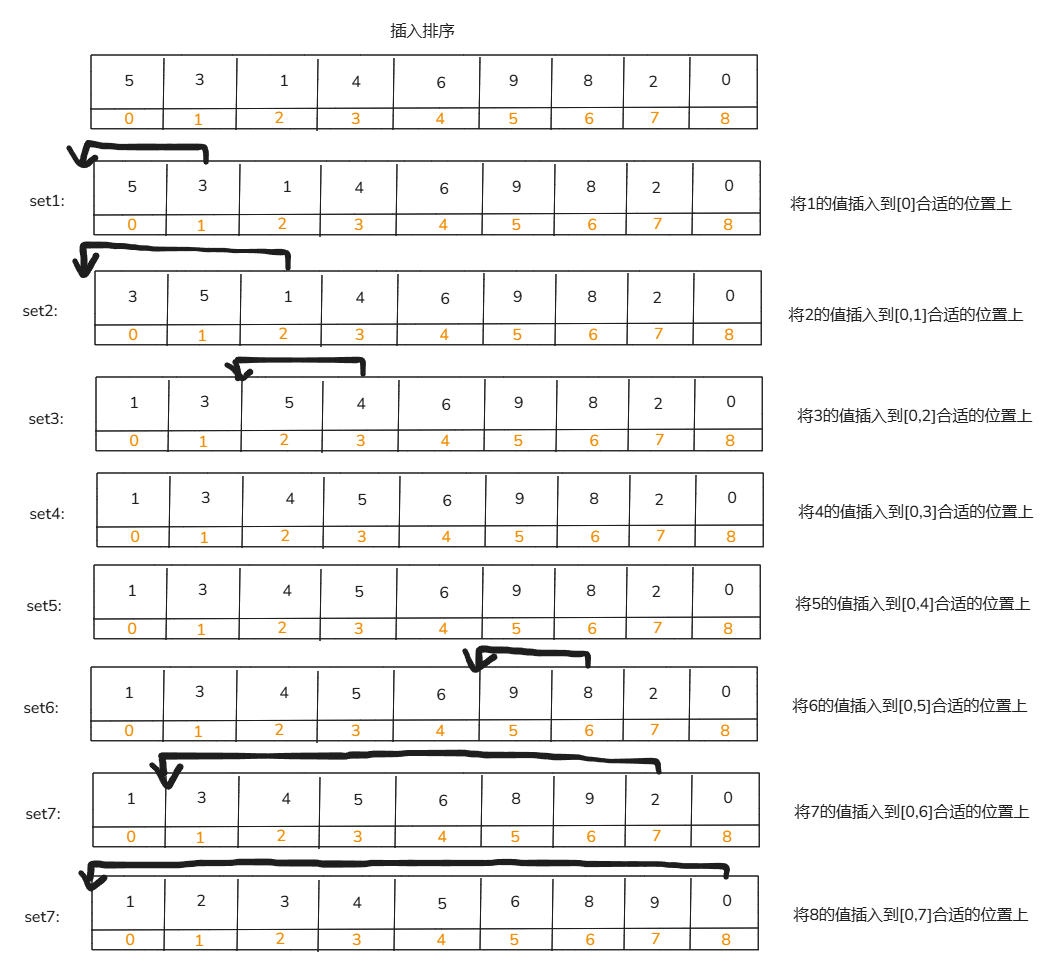
插入排序 第一步:将[0]排序;第二步:将[0,1]排序;第三步:将 [0,2]排序;第四步:将[0,3]排序……
具体插入实现方法(set7):
当我们到达set7时,[0,6]一定是有序的。所以从右往左一个一个比较
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 static void InsertionSort (int [] arr{ if (arr == null || arr.Length < 2 ) return ; for (int i = 1 ; i < arr.Length; i++) { for (int j = i - 1 ; j >= 0 && arr[j] > arr[j + 1 ]; j--) { Swap(arr, j, j + 1 ); } } }
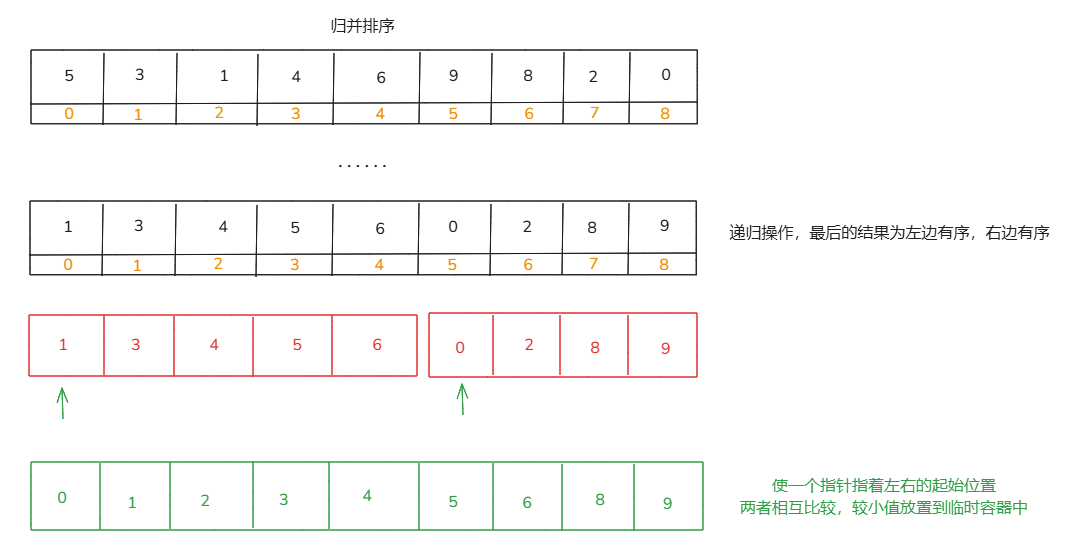
归并排序
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 static void MergeSort (int [] arr, int left, int right{ if (left >= right) return ; int mid = left + ((right - left) >> 1 ); MergeSort(arr, left, mid); MergeSort(arr, mid + 1 , right); merge(arr, left, mid, right); } static void merge (int [] arr, int L, int M, int R{ int [] temp = new int [R - L + 1 ]; int i = 0 , p1 = L, p2 = M + 1 ; while (p1 <= M && p2 <= R) temp[i++] = arr[p1] <= arr[p2] ? arr[p1++] : arr[p2++]; while (p1 <= M) temp[i++] = arr[p1++]; while (p2 <= R) temp[i++] = arr[p2++]; for (int j = 0 ; j < temp.Length; j++) arr[L + j] = temp[j]; }
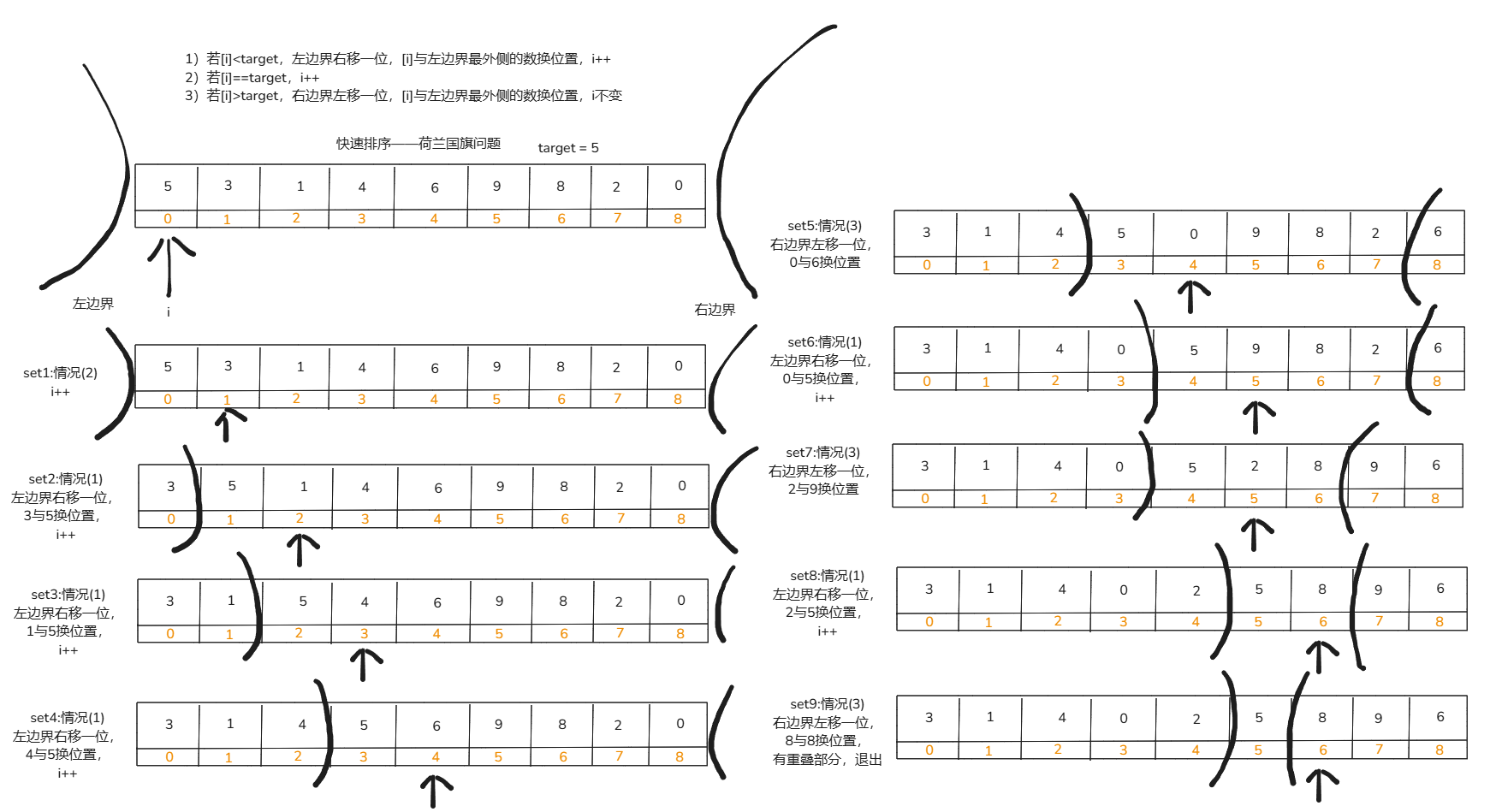
快速排序 在学习快速排序前先看一下荷兰国旗问题
现有一个数组arr和target,要求小于target的数放在数组左边,大于target的放在数组的右边,等于target的数放在中间
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 static void Partition (int [] arr, int target{ int left = -1 , right = arr.Length; int i = 0 ; while (i < right) { if (arr[i] < target) Swap(arr, ++left, i++); else if (arr[i] > target) Swap(arr, i, --right); else i++; } }
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 static void QuickSort (int [] arr, int L, int R{ if (L >= R) return ; int random = new Random().Next(R - L + 1 ); Swap(arr, L + random, R); int [] p = Partition(arr, L, R); QuickSort(arr, L, p[0 ] - 1 ); QuickSort(arr, p[1 ] + 1 , R); } static int [] Partition (int [] arr, int L, int R{ int less = L - 1 ; int more = R; while (L < more) { if (arr[L] < arr[R]) Swap(arr, ++less, L++); else if (arr[L] > arr[R]) Swap(arr, --more, L); else L++; } Swap(arr, R, more); return new [] { less + 1 , more }; }
二分法 在有序数列中查找某个值
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 static void fun (int [] arr, int target{ int m = arr.Length / 2 ; if (arr[m] == target) Console.WriteLine(m); else if (arr[m] > target) fun(arr[..m], target); else fun(arr[(m + 1 )..], target); }
在有序数列中查找最大值
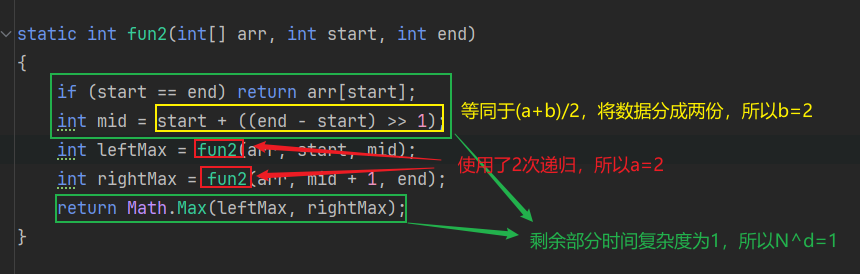
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 static int fun2 (int [] arr, int start, int end{ if (start == end) return arr[start]; int mid = start + ((end - start) >> 1 ); int leftMax = fun2(arr, start, mid); int rightMax = fun2(arr, mid + 1 , end); return Math.Max(leftMax, rightMax); }
递归方法的时间复杂度:
master公式的使用:
使用master公式的前提条件是在递归的时候平分数据 ,如fun2将数平方成了2份,也可以平分成3份、2/3份,只要是平分就行。
b:递归的时候,将数据平方成了多少份
d:除去递归函数外其他部分的时间
最终的结果为:
所以最后的时间复杂度为O(N)